Dog Bone, Joint & Muscle: Hip Surgery
Canine Bone Joint and Muscle QuickLinks
Anatomy:
The term “Hip” is used to mean joint. This joint is located in the lateral hind quarter of the body and is also known as the “Os coxae”. The head of the femur, which is almost round and spherical, is commonly called the “Ball”. It fits into a cavity of the pelvis called the “Acetabulum”. The acetabulum is a hollow, spherical cavity commonly called the “Socket”. This joint is generally called the “Ball & Socket” joint.
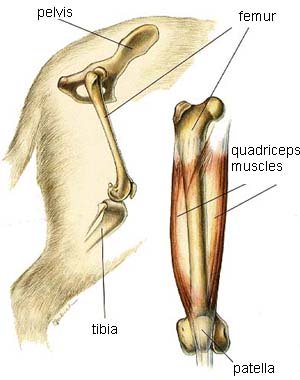
Picture of Dog Hip Joint
Pre Surgical Requirements:
Before a dog is operated on for any hip problem, there are some requirements to be fulfilled such as, weight reduction, sensitivity tests, monitored exercise and the implementation of a nutrition plan as prescribed by the operating veterinarian.
Types of Surgery:
Usually hip surgery in dog depends upon the condition of the canine hip area.
- Femoral Head Osteotomy (FHO) or Femora Head
Arthroplasty is indicated in conditions where head of femur is
dislocated in such a way that, no recovery is possible, like in an
automobile accident. The head of femur if is broken off from shaft
usually requires complete excision. Femoral head osteotomy is thus
performed to excise the head of femur completely.
- Canine Total Hip Replacement (THR) is usually
indicated for those conditions where osteotomy fails or either there
remains no other option. Advanced dog hip dysplasia can only be treated
by total hip replacement. This type of surgery is very effective, as it
completely replaces a diseased, fractured or abnormal hip joint with a
new, artificial joint. It is an expensive option of hip surgery, but is
very effective. This surgical option is very best for dog breeds having
weight over 40 pounds.
- Triple Pelvic Osteotomy (TPO) is usually performed in young dogs. Severe arthritis, dislocation of joint & dysplasia are some indications for this hip surgical option. In this type of surgery, the hip joint is made free to articulate by cutting the pelvis at three different sites, thus it is termed as triple pelvic osteotomy.
Post Operative Management of Surgery:
Once hip surgery is performed, management of the condition and some medications are usually required.
Non Steroid Anti Inflammatory Drugs are usually administered to overcome pain, fever and inflammatory cell infiltration to enhance early recovery.
Antibiotics may be administered to prevent any post surgical infection.
Nutritional supplements are helpful in recovery, but it should be ensured that the supplement would not cause any weight gain. Low energy nutritional supplements with more vitamins & minerals especially calcium in it will help in rapid recovery.
One natural homeopathic supplement that is made specifically to support the muscles and joints in dogs is PetAlive Muscle & Joint Support Formula. It is formulated to help with symptoms, relieve pain, reduce arthritis stiffness, rheumatism and degenerative joint disease in dogs.
Prognosis:
The prognosis for canine hip surgery is highly variable. In most of cases, the prognosis is very good. In replacement surgical options, the outcome it is variable depending upon the surgical procedures used, standards and replacement material.
In most cases, the rate of recovery is very high, but depends upon the condition of the dog being operated on.
|
|